Twospotted Spider Mite
Tetranychus urticaeT. urticae is one of the most economically important pests in a wide range of outdoor and protected crops worldwide. T. urticae uses its mouthparts to penetrate plant cells, notably on the undersides of leaves, and ingests their contents. Each minute 1-2 dozen cells can be destroyed this way. The first visible symptoms are small whitish speckles, mainly around the midrib and larger veins. When these spots merge, the empty cells give areas of the leaf a whitish or silvery-transparent appearance.
Due to its short life cycle, abundant progeny and arrhenotokous reproduction, T. urticae is able to develop resistance to acaricides very rapidly. As a result it is considered one of the “most resistant species” in terms of the total number of pesticides to which populations have become resistant, and its control has become problematic in many areas worldwide.
Twospotted Spider Mite resistance profile
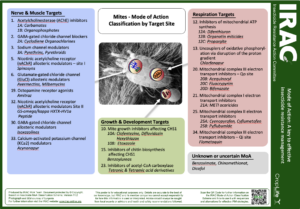
Known resistances:
- Carbamates – Group 1A
- Avermectins, Milbemycins – Group 6
- Clofentezine, Hexythiazox, Diflovidazin – Group 10A
- Oganotin miticides – Group 12B
- Acequinocyl – Group 20B
- METI acaricides & insecticides – Group 21A
- Unknown or uncertain MoAs – Group UN
| Species | Distribution | Chemical class | Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Pyrethroids-Pyrethrins (3A) | Target site point mutation (main) |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Pyrethroids-Pyrethrins (3A) | P450 monooxygenase (secondary) |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Clofentezine-Hexythiazox-Diflovidazin (10A) | cytochrome P450 and esterase |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Acequinocyl (20B) | Esterases (but probably not GST and P450 enzymes) |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | METI acaricides and insecticides (21A) | Oxidative metabolsim (MFOs) |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Carbamates (1A) | Metabolic: Esterases |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Organophosphates (1B) | AChE point mutations |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Avermectins-Milbemycins (6) | Metabolic: Glutamate S Trans-ferase (GST) inhibition |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Avermectins-Milbemycins (6) | Target site: point mutations on GluCl1 and GluCl3 channels |
| Tetranychus urticae | Worldwide | Organotin miticides (12B) | Oligomycin-sensitive Mg ATPase, Esterase isozymes, Oxidases |
| Tetranychus urticae | n/a | Tetronic and Tetramic acid derivatives (23) | Oxidative metabolism possible but field resistance not validated |
| Tetranychus urticae | Australia, USA | Amitraz (19) | P450 cytochrome monooxygenase, Modified target site. |